[ Free Consultation ] Are you interested in exploring wide-format scanner options? Get help from our top tech experts in a free consultation call. You will learn that the best technology fits your specific situation best.
Click Here to Schedule Your Free Consultation Call
Large-format scanning is instrumental for many AEC (architectural, engineering, & construction) companies.
Digital workflows are changing how construction documents are handled, viewed, marked up, and shared. But, you can still find vaults of printing architectural drawings that need to be digitized.
There are two primary types of wide-format scanning technologies to consider. Both have their merits, but it is a matter of application regarding which process suits your situation.
Read on to learn the difference between the two to determine which suits you best - CCD vs. CIS scanner technologies.

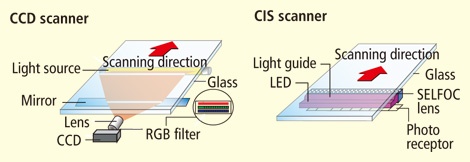
CCD Technology Scanner
CCD stands for Charged Coupled Device. This is the same imaging sensor found inside a legacy digital camera. CCD uses an actual lens to reduce the image onto the imaging sensor.
This method is excellent for capturing high-resolution details and widening color space. In many cases, CCD scanners are preferred when the highest image quality is paramount.
The fine detail in the CCD-type scanner makes it the scanner of choice for higher-resolution graphics and artistic applications. Still, it is common to see CCD types of large format scanners used for AEC or technical scans.
"Both CIS and CCD technologies have their merits, but it is a matter of application regarding which process suits your situation. "
Another benefit of CCD scanning is a greater depth of field. This is helpful if you plan to scan many folded sheets. With CCD technology, fold lines can be tweaked through the scanning software so they don’t image as much in the scanned file. CCD scanners also can scan "mounted" or thick originals.
Advantages of CCD Scanners
- High signal/noise ratio due to florescent lamp light source
- Relatively insensitive to focus depth due to cameras with apochromatic lenses
According to an industry-leading business technology website, p4photel - a resource center for imaging professionals, here are four reasons to consider a CCD technology scanner.
Image Quality and Flexibility
CCD scanning technology produces quality scans for virtually any type of document that will physically fit through the roll feed aperture.
Whether your original documents are hand-drawn engineering drawings, B&W photos, or maps, CCD scanner technology captures 16-bit grayscale (64,000 shades of grey). This process uses a dedicated monochrome channel for a much sharper, clearer image.
Conversely, CIS scanners only deliver an 8-bit grayscale (256 shades). This has some restrictions in cases like full bleed graphics and direct copy to 8 and 12-color printers.
In the exceptional cases of scanning GIS maps, blueprints with stiff edges, newspapers, delicate documents, or mylar film, a CCD scanner will give you a much more dynamic range and is therefore highly recommended.
Productivity
(Contex) CCD scanners take originals that are inserted face down. This is because the imaging sensors are positioned underneath the scanning surface.
Some argue that face-up scanning allows for better quality control, but it is a matter of user training. Face-down scanning is neither harder nor less accurate than the face-up orientation of most CIS scanners.
File transfer is an attribute of CCD scanners. These scanners can harness the full potential of USB 3.0 for file transfer. This guarantees that users experience virtually zero wait time for file transfer between images. So, if overall speed is what you are after, there is no denying that a CCD scanner is a better choice.
Color Fidelity
The inherent technical advantage of camera-based technology makes the color gamut much broader, color fidelity greater, and image noise reduced.
Since cameras capture up to 48-bit color, printing and copying to 8 or 12-color printers produce significantly better results than CIS. Color depth and the ability to recognize the nuances of gradients are superior on CCD scanners.
Thick Document and folded document Scanning
Scans of mounted originals up to .60” can be done with CCD scanners but not with (most) CIS scanners.
The reason for this is that the optics of the CIS technology do not image raised or uneven surfaces well. The CIS fiber optic lens array does not offer a deep depth of field. So, small nuances, like fold marks, will image on a CIS scan. If your documents include uneven surfaces, like folded prints, go with a CCD scanner for optimal results.
Disadvantages of CCD Scanners
- Higher equipment cost
- More complex and fragile technology
- Larger form factor than CIS types
- Typically require digital stitching of multiple image fields
- Lower optical resolutions
- Lens distortion can sometimes be a factor
What about CMOS Sensors?
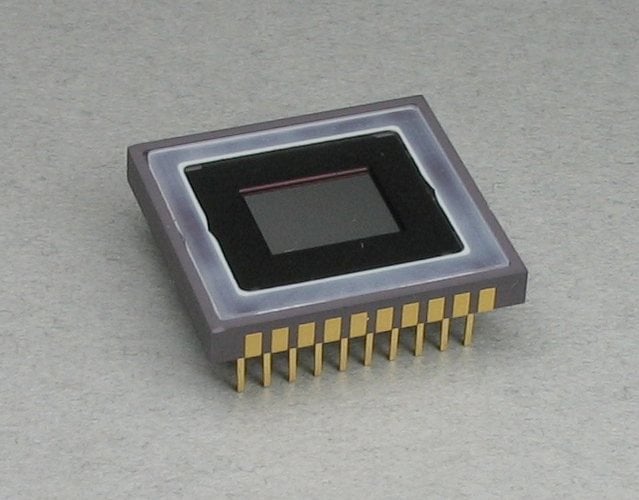

Sometimes, there is confusion regarding CDD and CMOS sensors since they are both based on an apochromatic lens focusing light on the capturing sensor.
In many ways, CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) has become more commonplace regarding the status quo. This is mainly due to their use of personal digital cameras.
If you look at the specs of just about any point-and-shoot or digital SLR camera, it is usually a CMOS device under the hood. Although both sensors (CCD and CMOS) start at the same point - converting light into electrons, some differences exist.
Reasons Why CCD Is Better For Large Document Scanning
- CCD sensors create high-quality, low-noise images.
- CMOS typically produces more noise.
- The light sensitivity of CMOS sensors tends to be lower.
- CMOS sensors use very little power. This is why they are excellent choices for hand-held cameras. On the other hand, CCDs require much more power, but they produce great images. The power trade-off is a moot point since CCD-based large-format scanners are stationary devices.
Overall, CCDs traditionally perform better in high-quality image environments. So, scanner manufacturers have stood by this technology rather than transitioning to a CMOS sensor.
Estimate the Savings of Large Format Scanning Jobs
Free online calculator
Determine projected costs and revenue of scanning jobs
Completely customizable for your specific needs

CIS Technology Scanner
Contact Imaging Sensor (CIS) is the other type of scanning technology. Instead of using a standard lens to reduce the original image onto the sensor, CIS technology incorporates many fiber optic lenses to transfer the original image information to an array of sensors.
CIS technology is less expensive than the traditional CCD models, but there can be some trade-offs regarding image quality, especially when scanning aerial photos or maps.
Since there are no cameras to calibrate and the sensors are controlled by software, there is much less maintenance with a CIS-based system.
But, because of the poor depth of field of optics, fold lines and wrinkles will image with CIS. Also, there is a reduction of color space information with CIS.
Unless you want to capture mainly primary colors, CIS could leave you wanting more.
But, remember that although the physical CIS technology has some limitations, many manufacturers have overcome this by deploying sophisticated software that compensates for the CIS shortcomings.
So, most of the time, a good case can be made for CIS versions, especially when budgets are constrained. CIS scanners have become the technology of choice for those needing blueprint scanners.
Advantages of CIS Scanners
- Less Cost
- High reliability
- More compact
- No stitching required
- Higher optical resolution
- No lens distortion
Disadvantages of CIS Scanners
- Sensitive to focus on depth
- Lower signal/noise ratio due to LED light source
CCD vs. CIS Takeaway
CIS is worthy of your consideration if you work with CAD/GIS drawings and want to scan them into a digital format. It is the more cost-effective solution, and new, robust software applications have narrowed the difference between CCD and CIS.
But, if your quality requirements are more demanding, such as photos or fine art, you should be looking at a CCD scanner. It will give you the absolute best image quality, hands down. Sure, it will be much more of an initial investment, but it will be well worth it.

You Can Count on TAVCO
In the complex landscape of AEC, you need a vendor as committed to quality and reliability as you are. TAVCO brings you just that—with high-performance tools like our durable large-format plotters, cutting-edge 3D scanners, and innovative software solutions.
We build long-term relationships fortified by unwavering support and innovative solutions that keep you ahead of the curve. Plus, when you have questions or need advice—including cost-effective options—you can always speak directly with a live TAVCO specialist, not a bot or an automated attendant.
👇👇👇
Ready to take the next step? Chat with a TAVCO specialist today to tailor solutions for your unique needs.
🛒 Or explore our range of products at www.tavcotech.com.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in 2011 and updated for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Content sources:
Contex Large Format Scanning
How Stuff Works (CCD and CMOS)National Azon
Art Post, P4PHotel
Tags:
Large format scanners
February 17, 2020




Comments